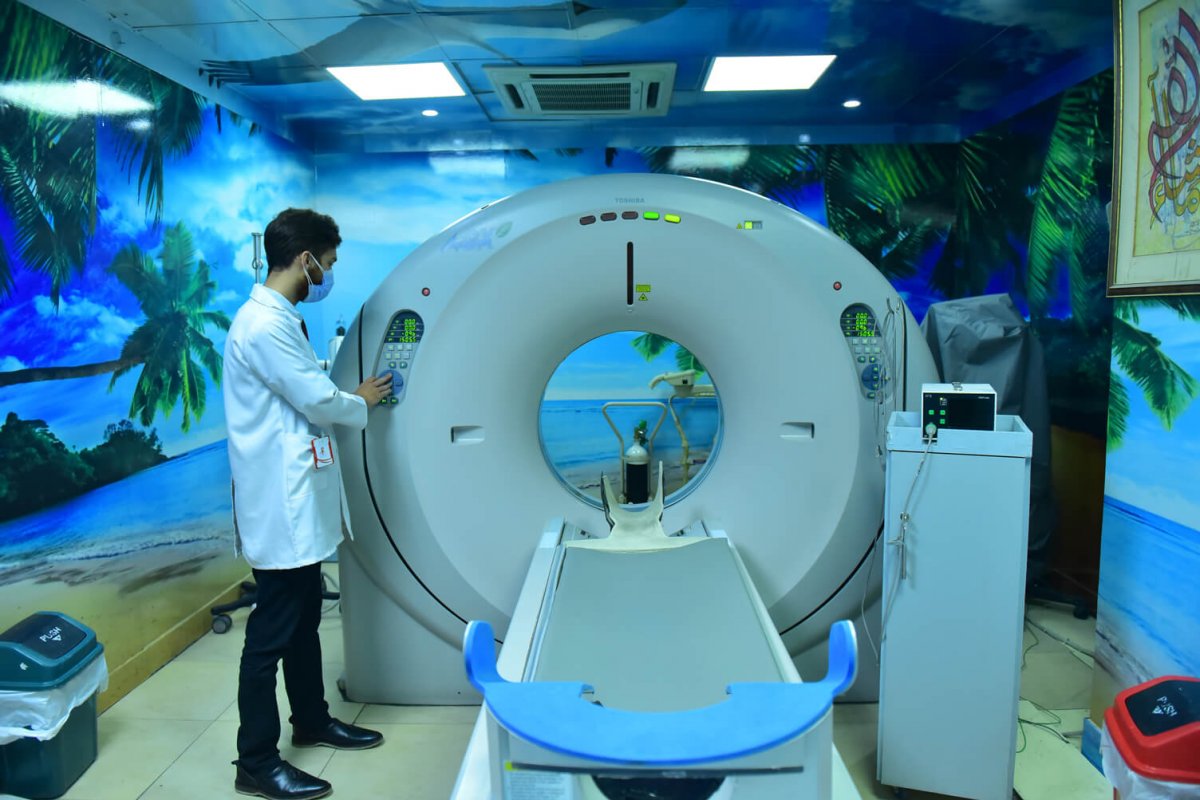
Computed tomography, also referred to as CT or CAT, enables others to see what is transpiring inside the human body. It is a diagnostic medical imaging testing use to replicate three-dimensional imaging of the human organs, bones, certain tissues as well as specific blood vessels. These are generated by combining multiple X-rays, which are automatically done by the computer attached during the examination. These cross-sectional images that are generated during this procedure, are reformatted and can be analyzed from different angles which enables medical examiners to have a better approach and understanding towards their patients. These images can be viewed on films or displayed on screens and media. CT methodology is efficient, painless and the most accurate procedure for problem analysis. With the advancement in technology, computed tomography is a trusted method to locate the different types of cancers since imaging allows the examiner to confirm the presence of a tumor. It makes it easier to determine the position of the tumor and how menacing it is, depending upon its size and location. In a certain catastrophic situation, CAT is used to determine the location of internal bleeding regions which allows the doctors to handle them immediately and save the person in distress.
There are various CAT procedures, each having a specific procedure as well as risks. Some computed tomography that is being commonly being used includes
- CT Scan Abdomen
- CT Angiography
- CT Scan Arthrography
- CT Scan Bones
- CT Scan Brain/ CT Scan Head
- CT Scan Chest (CT Scan Lung)
- CT Scan Neck
- CT Scan Pelvis
- CT Scan Renal Stones
- CT Scan Sinus
- CT Scan Spine
These are low-dose CAT scans that are offered in many hospitals around the world. As the pandemic is upon us, doctors are mostly focusing on HRCT, as it is one of the most efficient and fastest ways to identify the presence of virus inside the body and how much has it damaged the body.
Chest CT is mainly used to examine any abnormalities found in a regular chest x-ray. It is used to reason the unexplainable behavior that is associated with the lungs somehow, for instance, shortness of breathing or severe chest pains. Chest CT can identify small nodules in the lungs which can identify lung cancer at the very beginning stage. These scans help oncologists to plan their patient’s chemotherapy and see whether they are responding to the treatment. Malignant Tumors, Tuberculosis, Pneumonia, and many other respiratory diseases can be identified using this methodology.
HRCT is a high-resolution computed tomography that identifies disease better than conventional radiology. HRCT is used for the diagnosis and assessment of Interstitial lung diseases, such as pulmonary fibrosis, interstitial pneumonitis, and other generalized lung diseases such as emphysema, bronchiectasis. Where HRTC is unable to identify the cause of the problem a biopsy is necessary.
To prepare a patient for a CT scan, they are required to wear a medical gown provided by the hospital facilities. All metallic objects that might hinder the scans are required to remove which includes hairpins, piercing, or removable pieces of dental ware. In the case of female patients, they are required to remove their bra as it has metal wires inside them. Few hours before the procedure, doctors ask the patients to abstain from drinking, eating, or consuming anything. They might alter with the reading of the scan. The medical examiner must be aware of any history of illness that a patient might have, for instance, heart disease, asthma, or thyroid problems. They are required to report any allergies or any sort of medication they might be using. Any of these conditions might increase the risk of an adverse effect. Women should inform the CT technologist if they might be expecting a child shortly soon to prevent any complications during their pregnancies.
After being identified with all the required information for the patient, they are required to move to a separate room where the CT scanner is present. The patient has to lie on a narrow table, strapped to maintain position, which slides them inside the tube of the CT scanner. X-ray tubes and detectors are located on a tube called a gantry which rotates around the patient. The workstation is located in a separate room which receives all the imaging being captured by the gantry. The technologist operates the scanner from the control room and monitors your exam in direct visual contact. They will be able to communicate using a speaker and microphone.
Each body part absorbs a different amount of radiation which makes it possible for the doctors to identify the organ. Several x-ray beams circulate to the patient who absorbs them. Sometimes the table moves so x rays can make a spiral path for better imaging. Special computers present in the control rooms log in three-dimensional images and their slices are displayed on the monitors. Each slice shows the interior of the body in a detailed manner, giving the human body a multi-dimensional aspect. Each rotation provides multiple imaging resulting in more detail and additional capabilities.
To obtain results, the patient must refer to a radiologist. A radiologist will be supervising the patient’s exams throughout the entire procedure. They will analyze the images obtained from the CAT examination and send an official report who has ordered the examination. If any follow-up examinations are required, the doctor handling the patient’s case will notify them. Follow-up examinations are used to further identify the abnormalities in the patient tomography. In the case of a recovering patient, they are used to check if the abnormality is stable or changing.
Computed tomography has certain risks. With exposure to an extensive amount of radiation, there is a possibility of cancer. But the benefits of the diagnosis outweigh the chance of having cancer. The risk of serious allergic reaction to contrast materials that contain iodine is extremely rare, and radiology departments are well-equipped to deal with them. Children are more sensitive to radiation; they should have a CT exam only if it is essential for making a diagnosis and should not have repeated CT exams unless absolutely necessary. CT scans in children should always be done with a low-dose technique. As for unborn children and pregnant women, CT scans are not recommended unless medically necessary, by the approval of a doctor because they might harm the fetus. However, the benefits outweigh the risks here as this procedure is fast as time is of the essence for a patient. Explanatory surgeries are no longer needed to be conducted and the precise location of tumors can easily be located. It is indeed a milestone in medicine.